The Pistil, Megasporangium and Embryo sac
The Pistil, Megasporangium and Embryo sac: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Megasporogenesis, Nucellus, Apocarpous Pistil & Plant Ovary etc.
Important Questions on The Pistil, Megasporangium and Embryo sac
In the given figure of embryo sac, choose the option that is correctly showing the parts (1), (2), (3) and (4).
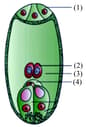
Which of the following represents the persistant remains of nucellus ?
The megaspores are formed from megaspore mother cell that are produced in which of the following region of ovule:
Which of the following pairs has haploid structures?
Embryo sac occurs in
Enclosed within the integuments is a mass of cells is called
Assertion: Megaspore mother cell undergoes meiotic divisions to produce four megaspores.
Reason: Megaspore mother cell is diploid and megaspores are haploid.
The below diagram shows the mature embryo sac of plants.
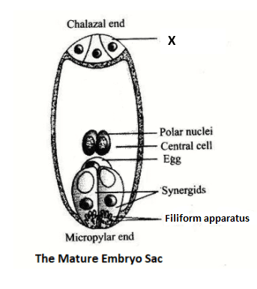
Identify the correct function of the part labelled as 'X'.
Draw and label the chalazal end of an embryo sac.
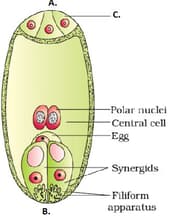
The egg apparatus is present opposite to the _____ (micropylar end/chalazal end).
State one function of the chalazal end.
Chalazal end of a female gametophyte has egg cells.
Which label in the given picture out of A, B, and C represents chalazal end of a female gametophyte.
Leguminosae family has _____ (monocarpellary/multicarpellary) gynoecium.
Bicarpellary gynoecium is present in the family Solanaceae.
Write one difference between the monocarpellary flower and multicarpellary flower.
Multicarpellary gynoecium can be syncarpous or apocarpous.
Antipodal cells are:
There are three antipodal cells which are _____ (haploid/triploid).
Select the correct option for the given picture.